Science
(Chapter – 3) (METALS AND NON METALS )
(Class – X)
Question 1:
Which of the
following pairs will give displacement reactions?
(a) NaCl solution and
copper metal
(b) MgCl2
solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4
solution and silver metal
(d) AgNO3
solution and copper metal.
Answer 1:
(d) AgNO3
solution and copper metal
Question 2:
Which of the following methods
is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
(a) Applying grease
(b) Applying paint
(c) Applying a
coating of zinc
(d) All of the above.
Answer 2:
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(We can also apply grease and paint to prevent iron
from rusting. However, in case of iron frying pan, grease and paint cannot
be applied because
when the pan will
be heated and washed again and again,
the coating of grease and paint would get destroyed.)
Question 3:
An element reacts
with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point.
This compound is also soluble in water. The element
is likely to be
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
Answer 3:
(a) The element is likely to be calcium.
Question 4:
Food cans
are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a)
zinc is costlier than tin.
(b)
zinc has a higher
melting point than tin.
(c)
zinc is more reactive
than tin.
(d)
zinc is less reactive
than tin.
Answer 4:
(c) Food cans are
coated with tin and not with zinc because zinc is more reactive than tin.
Question 5:
You are given a hammer,
a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non
- metals.
Answer 5:
(a)
With the hammer, we can beat the sample and if it can be beaten into thin sheets (that is, it is malleable), then it is a metal otherwise a non-metal. Similarly, we can use the battery,
bulb, wires, and a switch
to set up a circuit
with the sample. If the sample conducts
electricity, then it is a metal otherwise
a non-metal.
(b)
The above tests are useful in distinguishing between
metals and non-metals as these are based
on the physical properties. No chemical reactions
are involved in these tests.
Question 6:
What are amphoteric
oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer 6:
Those oxides that behave as both acidic and basic oxides are called amphoteric oxides.
Examples: aluminium oxide
(Ah03)
Al203 + 6HC1 -------> 2A1Cl + 3H20 basic
Al203 + 2NaOH .........> 2NaA102 + H20 acidic
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is also an amphoteric oxide.
Question 7:
Name two metals which will displace
hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Answer 7:
Metals that are more reactive
than hydrogen displace
it from dilute acids. For example:
sodium and potassium.
Metals that are less reactive
than hydrogen do not displace it. For example: copper and silver.
Question
8:
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer 8:
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M: Anode Impure metal M
Cathode Thin strip of pure metal M Electrolyte Solution of salt of the metal M
Question 9:
Pratyush took sulphur
powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting
a test tube over it, as shown in figure below.
What will be the action of gas on
(i)
dry litmus paper?
(ii)
moist litmus paper?
(b) Write a balanced
chemical equation for the reaction
taking place.
Answer
9:
(a) (i) There will be no
action on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Since the gas is sulphur dioxide (SO2), it turns
moist blue litmus paper to red because sulphur dioxide reacts with moisture to
form sulphurous acid.
(b)
s𝑢𝑙𝑝ℎ𝑢𝑟 𝑑𝑖𝑜𝑥𝑖𝑑𝑒
𝑆𝑂2 (𝑔) + 𝐻2𝑂 (𝑙) → 𝐻⏟ 2 𝑆𝑂 3 (𝑎 𝑞)
𝑆𝑢𝑙𝑝ℎ𝑢𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑
Question 10:
State two ways to
prevent the rusting of iron.
 Answer
10:
Answer
10:
Two ways to prevent the
rusting of iron are:
Oiling, greasing, or painting: By applying
oil, grease, or paint, the surface
becomes water proof and the moisture and oxygen present
in the air cannot come into
direct contact with iron. Hence, rusting is
prevented.
Galvanisation:
An iron article is coated with a layer of zinc
metal, which prevents the iron to come in contact with oxygen and moisture.
Hence, rusting is prevented.
Question 11:
What type of oxides is formed when non-metals combine
with oxygen?
 Answer
11:
Answer
11:
Non-metals
combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides. For example:
𝑆(𝑠) + 𝑂2 (𝑔) → 𝑆⏟𝑂 2 ( 𝑔)
𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑𝑖𝑐
𝑖𝑛 𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒
Question 12:
Give reasons
(a) Platinum, gold
and silver are used to make jewellery.
(c) Aluminium is a
highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and
sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
 Answer
12:
Answer
12:
(a)
Platinum, gold, and silver are used to make jewellery
because they are very
lustrous. Also, they are very less reactive and do not corrode easily.
(b)
Sodium, potassium, and lithium are very reactive
metals and react very vigorously with air as well as water. Therefore, they are
kept immersed in kerosene oil in order to prevent their contact with air and moisture.
(c)
Though aluminium is a highly reactive metal, it is
resistant to corrosion. This is because aluminium reacts with oxygen present in
air to form a thin layer of aluminium oxide. This oxide layer is very stable
and prevents further reaction of aluminium with oxygen. Also, it is light in
weight and a good conductor of heat. Hence, it is used to make cooking utensils.
(d)
Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted
into oxides during the process of extraction because metals can be easily
extracted from their oxides rather than from their carbonates and sulphides.
Question 13:
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being
cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are
effective in cleaning the vessels.
 Answer
13:
Answer
13:
Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in air to form
copper carbonate and as a result, copper
vessel loses its shiny brown surface forming
a green layer
of copper carbonate. The
citric acid present in the lemon or tamarind neutralises the basis copper carbonate
and dissolves the layer. That is why, tarnished copper vessels are cleaned with
lemon or tamarind juice to give the surface of the copper vessel its
characteristic lustre.
Question 14:
Differentiate between metal and
non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
metal |
non metal |
Metals
are electropositive.
|
Non-metals
are electronegative.
|
They
react with oxygen to form basic oxides.
4𝑁𝑎 + 𝑂2 → 2𝑁𝑎2 𝑂
These
have ionic bonds.
|
They
react with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides.
𝐶 + 𝑂2 → 𝐶𝑂2
These
have covalent bonds.
|
They react with water to form oxides and
hydroxides. Some metals react with cold water, some with hot water,
and some with steam.
2𝑁𝑎 + 2𝐻2𝑂 → 2𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 + 𝐻2 ↑
|
They do
not react with water.
|
They react with dilute acids to form a salt and evolve hydrogen gas.
However, Cu, Ag, Au, Pt, Hg do not react.
2𝑁𝑎 + 2𝐻𝐶𝑙 → 2𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 + 𝐻2 ↑
|
They do not react with dilute acids.
These are not capable of replacing hydrogen.
|
They react with the salt solution of metals. Depending on their
reactivity, displacement reaction can occur.
2𝐶𝑢𝑆𝑂4 + 𝑍𝑛 → 𝑍𝑛𝑆𝑂4 + 𝐶𝑢
|
These
react with the salt solution of non-metals.
|
They
act as reducing agents (as they can easily lose electrons).
𝑁𝑎 → 𝑁𝑎+ +
𝑒−
|
These
act as oxidising agents (as they can gain electrons).
𝐶𝑙2 + 2𝑒− → 𝐶𝑙−
|
Metals
are electropositive.
|
Non-metals
are electronegative.
|
They
react with oxygen to form basic oxides.
4𝑁𝑎 + 𝑂2 → 2𝑁𝑎2 𝑂
These
have ionic bonds.
|
They
react with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides.
𝐶 + 𝑂2 → 𝐶𝑂2
These
have covalent bonds.
|
They react with water to form oxides and
hydroxides. Some metals react with cold water, some with hot water,
and some with steam.
2𝑁𝑎 + 2𝐻2𝑂 → 2𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 + 𝐻2 ↑
|
They do
not react with water.
|
They react with dilute acids to form a salt and evolve hydrogen gas.
However, Cu, Ag, Au, Pt, Hg do not react.
2𝑁𝑎 + 2𝐻𝐶𝑙 → 2𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 + 𝐻2 ↑
|
They do not react with dilute acids.
These are not capable of replacing hydrogen.
|
They react with the salt solution of metals. Depending on their
reactivity, displacement reaction can occur.
2𝐶𝑢𝑆𝑂4 + 𝑍𝑛 → 𝑍𝑛𝑆𝑂4 + 𝐶𝑢
|
These
react with the salt solution of non-metals.
|
They
act as reducing agents (as they can easily lose electrons).
𝑁𝑎 → 𝑁𝑎+ +
𝑒−
|
These
act as oxidising agents (as they can gain electrons).
𝐶𝑙2 + 2𝑒− → 𝐶𝑙−
|
Question 15:
A man went door to door posing as a
goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold
ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution.
The bangles sparkled
like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile
argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out
the nature of the solution he had used?
 Answer
15:
Answer
15:
He must have dipped the gold metal in
the solution of aqua regia − a 3:1 mixture of
conc. HCl and conc. HNO3. Aqua regia is a fuming,
highly corrosive liquid.
It dissolves gold in it. After dipping the gold ornaments in aqua regia,
the outer layer of gold gets dissolved and the
inner shiny layer appears. That is why the
weight of gold ornament reduced.
Question 16:
Give reasons why copper is used to
make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
 Answer
16:
Answer
16:
Copper does not react with cold water,
hot water, or steam. However, iron reacts with steam. If the hot water tanks
are made of steel (an alloy of iron), then iron would react vigorously with the
steam formed from hot water.
That is why
copper is used to make hot water tanks, and not steel.
(i)
The reaction
of calcium with water is exothermic but the heat evolved is not sufficient
for the hydrogen to catch fire.
Ca(s) + 2H20(l) Ca(OH)i(aq) + H2(g)
Calcium starts floating because
the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
Potassium react violently with cold
water
and its reaction
is
so violent and exothermic that the evolved
hydrogen immediately catches
fire.
2K(s) + 2H20(l) 2KOH( aq) + H2(g) + heat energy
Question 3:
|
|
metal
|
iron sulphate
|
cupper ii sulphate
|
zinc sulphate
|
silver nitrate
|
|
A
|
No reaction
|
Displacement No reaction
|
|
|
|
B
|
Displacement No reaction
|
|
No reaction
|
|
|
C
|
No reaction
|
No reaction
|
No reaction
|
Displacement No reaction
|
|
D
|
No reaction
|
No reaction
|
No reaction
|
No reaction
|
Use the Table above to answer the following
questions about metals A, B, C and D.
(i)
Which is the most reactive metal?
(ii)
What would you observe
if B is added to a solution
of Copper (II) sulphate?
(iii)
Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer 3:
(i) As per reactivity series, Iron is most reactive
metal among Iron, Silver and Copper. Since B can displace Iron from its sulphate, so B is the most reactive metal.
(ii) As B is more reactive
than Iron (As discussed in answer (i)), so it will displace
Copper from its Copper Sulphate
solution.
(iii) B is most reactive as discussed in part (i) and D is the least reactive
metal as unable to displace any of the solutions. Copper is more reactive than Silver and metal A can displace
Copper, so A is more reactive than C.
Hence, the order of decreasing
reactivity is B > A > C > D.
Question 4:
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction
when iron reacts with dilute H2S04.
Answer 4:
When reactive metals react
with
dilute hydrochloric acids, gives
a
salt
and hydrogen gas
Metal + Dilute acid Salt + Hydrogen
Reaction between Iron and H2S04:
Question 5:
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution
of iron (II) sulphate? Write the chemical
reaction that takes place.
·Answer 5:
Zinc is more reactive than Iron. When Zn is added to Iron (II) Sulphate, Zinc displaces Iron from its solutions and Zinc sulphate
is formed.
Zn( s) + FeS04( aq) ZnS04( aq) + Cu( s)
Question 1:
(i) Write the electron-dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
Answer 1:
(i) Electron - dot structure for Sodium:
Electron - dot structure for Oxygen:
Answer 2:
(i) Mineral:
(ii). Ore:
(iii). Gangue:
Answer 2:
Question 3:
Answer 3:
Electron - dot structure for Oxygen:
Question 2:
Why do ionic compounds have high melting
points?
Answer 2:
Ionic compounds have high melting
and boiling points. Because ionic compounds
are formed by the attraction
force of two opposite ions and a considerable amount of energy is required
to break this strong inter-ionic attraction.
Question
1:
Define the following
terms.
(i) Mineral
(ii)
Ore
(iii) Gangue.
Answer 1:
(i) Mineral:
The elements or compounds, which occur naturally
in the earth's crust, are known as minerals.
(ii). Ore:
If minerals contain a very high percentage of a particular metal and the metal can be profitably extracted from it. These minerals
are called ores.
(iii). Gangue:
Ores mined from
the earth are usually
contaminated
with
large
amounts
of impurities
such as soil, sand, etc., called gangue.
Question 2:
Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer 2:
The metals which are the least reactive,
they are often found in a
free state.
For example:
Gold, silver, platinum
and copper are found in the free state.
Question 3:
What chemical process
is used for obtaining a metal from its
oxide?
Answer 3:
> Metals low in the activity series are very unreactive. The oxides of these
metals can be reduced
to metals by heating alone.
heat
2Hg0(s)---2Hg(l) + O(g)
The metals in the middle of the activity
series such as iron, zinc,
lead, copper, etc., are moderately reactive. These metal oxides are reduced
to the corresponding metals by using suitable
reducing agents
ZnO(s) + C(s)---Zn(s) + CO(g)
> The metals high up in the reactivity series are very reactive. They are separated
from their oxides by electrolysis process.
Question 1:
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals.
metal zinc magnesium copper
Zinc oxide
Magnesium oxide
Copper oxide
answer 1:
Magnesium is the most reactive among
these three metals
and Zinc is more reactive
than Copper. So, Magnesium will displace Zinc oxide and Copper oxide whereas Zinc will displace
Copper oxide only.
metal
|
zinc
|
magnesium
|
cupper
|
Zinc oxide
|
no reaction
|
displacement
reaction
|
no reaction
|
Magnesium oxide
|
no
reaction
|
no reaction
|
no reaction
|
Copper oxide
|
displacement reaction
|
displacement
reaction
|
no reaction
|
Question 2:
Which metals do not corrode
easily?
Answer 2:
The metals which are the least reactive,
do not corrode easily.
For example:
Gold, silver, platinum
and copper.
Question 3:
What are alloys?
Answer 3:
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non metal.
For example:
> Stainless steel is an alloy of Nickel and Chromium.
> Amalgam is an alloy of Mercury.
> Brass is an alloy of Copper and Zinc.
> Bronze is an alloy of Copper and Tin.
> Solder is an alloy of Lead and Tin.
Question 1:
Ethane, with the molecular formula
C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
(c) 8 covalent bonds.
(d) 9 covalent bonds.
Answer 1:
(b) Ethane has 7 covalent
bonds.
Question 2:
Butanone is a four-carbon compound
with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid.
(b) aldehyde.
(c) ketone.
(d) alcohol.
Answer 2:
(c) The functional group of butanone
is ketone.
Question 3:
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a)
the food is not cooked
completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning
completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer 3:
(b) While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting
blackened on the outside, then it means that the fuel is not burning completely.
Question 4:
Explain the nature
of the covalent
bond using the bond formation
in CH3Cl.
Answer 4:
Carbon can neither lose four of its electrons
nor gain four electrons as both the processes require extra amount of energy and would make the system
unstable. Therefore, it completes its octet by sharing its four electrons
with other carbon
atoms or with atoms of other elements. The bonds that are formed by sharing electrons
are known as covalent bonds. In covalent
bonding, both the
atoms share the valence
electrons, i.e., the shared electrons belong to the valence
shells of both the atoms.
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons
to complete its octet, while
each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine
requires an electron
to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons
and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
Question 5:
Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid.
(b) H2S.
(c) propanone.
(d) F2.
Answer 5:
(d) F2
Question 6:
What is a homologous series? Explain
with an example.
Answer 6:
A homologous series is a series
of carbon compounds that have different
numbers of carbon atoms but contain
the same functional group.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all
part of
the
alkane homologous series. The general formula
of this series
is CnH2n+2.
Methane CH4
Ethane CH3CH3
Propane CH3CH2CH3
Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
It can be noticed that there is a difference of −CH2 unit between each successive compound.
Question
7:
How can ethanol
and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical
and chemical properties?
Answer 7:
ü Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant
odour while ethanoic acid has vinegar-like smell. The melting point of ethanoic acid is 17°C. This is below room temperature and hence, it freezes
during winters.
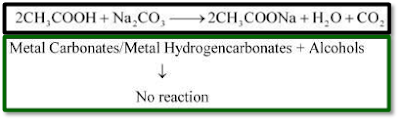
ü 
Ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates to form salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas while ethanol does not react with them.

Ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates to form salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas while ethanol does not react with them.
For example,
Question 8:
In the electrolytic refining
of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer
8:
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M:
Anode
|
→
|
Impure metal
M
|
Cathode Electrolyte
|
→
→
|
Thin strip
of pure metal M Solution of salt of the metal
M
|
Question 9:
Why are carbon and its compounds
used as fuels for most applications?
Answer 9:
Most of the carbon compounds
give a lot of heat and light when burnt in air. Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a clean flame and no smoke
is produced. The carbon compounds, used as a fuel,
have high calorific values. Therefore, carbon and its
compounds are used as fuels for most applications.
Question 10:
Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer 10:
Soap does not work properly
when the water is hard. A soap is a sodium
or potassium salt of long chain fatty acids. Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. When soap is added to hard water, calcium and magnesium
ions present in water displace sodium
or potassium ions from the soap molecules forming an insoluble substance called scum. A lot of soap is wasted in the process.
Question 11:
What change
will you observe if you test soap with litmus
paper (red and blue)?
Answer 11:
Since soap is basic in nature,
it will turn red litmus blue. However, the colour of blue litmus will remain blue.
QUestion 12:
What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer 12:
Hydrogenation is the process
of addition of hydrogen. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are added with hydrogen
in the presence of palladium and nickel catalysts
to give saturated hydrocarbons.
This reaction
is applied in the hydrogenation of vegetables oils, which contain
long chains of unsaturated
carbons.
Question 13:
Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo
addition reactions: C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer 13:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo
addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons, C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions.
Question 14:
Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter
and cooking oil.
Answer 14:
Butter contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot
be hydrogenated. On the other hand, oil has unsaturated fats. That is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated
fats (solids).
Question 15:
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer 15:
Cleansing action of soaps:
The dirt present on clothes
is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing
with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle
formation and trap the dirt at the centre
of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water.
Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.
Question 1:
What would be the electron
dot structure of carbon
dioxide which has the formula
CO2?
Answer 1:
Electron dot structure of CO2 is
Question 2:
What would be the electron
dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint − the eight atoms of sulphur
are joined together in the form of a ring.)
Answer 2:
Electron dot structure of a sulphur molecule
Question 1:
How many structural isomers
can you draw for pentane?
Answer 1:
Three structural isomers are possible for pentane.
Question 2:
What are the two properties of carbon
which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer 2:
The two features
of carbon that give rise to a large number of compounds are as follows:
(i) Catenation: It is the ability
to form bonds with other atoms of carbon.
(ii) Tetravalency: With the valency of four,
carbon is capable of bonding
with four other atoms.
Question
3:
What will be the formula and electron
dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer 3:
The formula for cyclopentane is C5H10. Its electron
dot structure is given below.
Question 4:
Draw the structures for the following compounds.
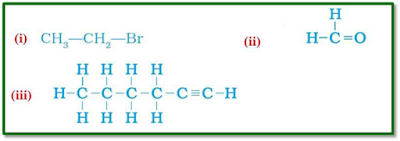
(i) Ethanoic acid (ii) Bromopentane*
(iii) Butanone (iv) Hexanal
*Are structural isomers
possible for bromopentane?
I)
.
( III)
(IV)
Question 5:
How would you name the following compounds?
Answer 5:
(i). Bromoethane (ii). Methanal
(iii). Hexyne
Question 1:
Why is the conversion of ethanol
to ethanoic acid an oxidation
reaction?
Answer 1:
Since the
conversion of ethanol
to ethanoic acid involves the addition of oxygen to ethanol, it is an oxidation reaction.
Question 2:
A mixture
of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding.
Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer 2:
When ethyne is burnt in air, it gives a sooty flame. This is due to incomplete combustion caused by limited supply of air. However, if ethyne is
burnt with oxygen,
it gives a clean flame with temperature 3000°C because of complete combustion. This oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding. It is not possible to attain such a high temperature without mixing oxygen.
This is the reason why a mixture
of ethyne and air is not used.
Question 1:
How would you distinguish experimentally between
an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Answer 1:
We can distinguish between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of their reaction with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. Acid reacts with carbonate and hydrogen carbonate to evolve
CO2 gas that turns lime water milky.
Alcohols, on the other hand, do not react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates.
Question 2:
What are oxidising agents?
Answer 2:
Some substances such as alkaline
potassium permanganate and acidified potassium dichromate are capable of adding oxygen
to others. These are known as oxidising agents.
Question 1:
Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Answer 1:
Detergents are ammonium
or sulphonate salts of long chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soap, they do not react with calcium and magnesium ions present in
hard water to form scum. They give a good amount
of lather irrespective of whether
the water is hard
or soft. This means that detergents can be used in both soft and hard water. Therefore, it cannot be used to check whether
the water is hard or not.
Question
2:
People use a variety of methods
to wash clothes. Usually after adding
the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub
with a brush or the mixture
is agitated
in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary
to get clean clothes?
Answer 2:
A soap molecule has two parts namely hydrophobic and hydrophilic. With
the help of these, it attaches to the grease or dirt particle and forms a cluster called
micelle. These micelles remain suspended as a colloid. To remove these micelles (entrapping the dirt), it is necessary to agitate
clothes.


























No comments:
Post a Comment
please do not enter any spam in the comment box.